Task Manager is one of the more important Windows utilities, built to manage program priorities, enable/disable services, and a whole lot more. With it, you can monitor your system’s resource usage, and even determine which programs or processes can be disabled in order to salvage what’s left of a slowing system.
Knowing how to run the Task Manager is essential if you’re going to make these changes, especially from the Command Prompt. Here is all you need to know about starting Task Manager from the Command Prompt, its shortcuts, and how to run it as an administrator, even if you have a standard account type.
Related: How to Reset Taskbar in Windows 10
Method 1: Task Manager Shortcuts
Shortcuts are a boon to any power user looking to access specific applications and interfaces with simple key combinations and a few clicks. Here are the shortcuts for the Task Manager.
1. Hotkey combinations
There are a couple of hotkey combinations that users ought to know to run Task manager in a snap.
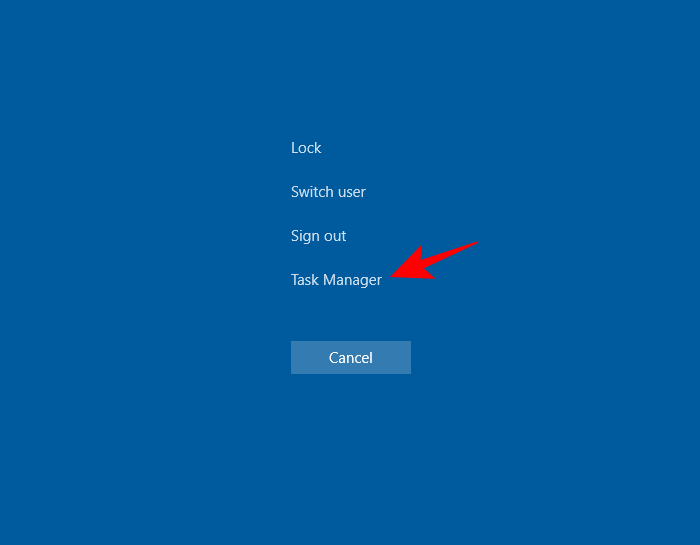
- Ctrl+Alt+Del – This key combination brings up a screen containing multiple shortcuts, including one for the Task Manager. Simply click on Task Manager to access it.
- Ctrl+Shift+Esc – This hotkey combination opens up the Task Manager instantly without you having to go through an additional screen, and as such is the fastest way to get to Task Manager.
Pressing Win+Xbrings up the hidden Power User Menu that has a variety of shortcuts to System settings and utilities.
Here, you can either click on Task Manager or simply press T to open the Task Manager.
The Taskbar on Windows provides one of the simplest ways to open the Task Manager. Simply right-click on the taskbar and select Task Manager.
Method 2: Run Task Manager from Command Prompt
Needless to say, we have to run the command prompt first in order to run Task Manager through it. Here’s how to go about it:
- Press
Win+Rto open the RUN box, type in “cmd” and hit Enter.
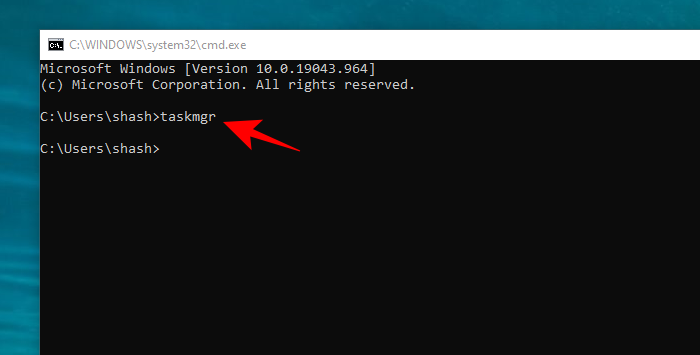
- Once the Command Prompt opens, type in taskmgr and press Enter to run the task manager:
This is the basic process of running the task manager from the command prompt. If you’re using an administrator account, you should have no problem going through these steps.
But what if you’re operating a standard account and still want to access the task manager via the command prompt, follow the guide below.
Method 3: Run Task Manager from Command Prompt as Administrator
Without administrator privileges, one is bound to run into “Access denied” error messages when trying to make changes using the task manager. There are a couple of ways that a standard account user can access the command prompt with administrator privileges. Here they are:
1. From a Standard Account (with admin password)
If you are the admin making changes on a standard account, all you have to do is run an elevated instance of the command prompt. Here’s how to do so:
- Press Start, type “cmd”, and click on Run as administrator.
- When prompted, enter the password and you’re good to go.
- Now, simply type in the taskmgr in CMD and run the task manager as before.
2. Access the built-in Administrator (without admin password)
Sometimes, the task manager is outright blocked by the administrator, and there is little that one can do without the admin’s password. But there is a nifty workaround that lets you access the built-in administrator, which can be used to do all kinds of things, including giving your standard account complete administrative rights, changing registry files, unblocking the task manager, and much more. For a complete guide on how to access this built-in administrator, follow this link.
Once you have followed those steps and have given your account administrator privileges it’s time to make the necessary changes to ensure that the task manager is not blocked for your account.
3. Unblock Task Manager using ‘Group Policy Editor’
If you have Windows 11 Pro, Enterprise, or Education Edition, you can use the Group Policy Editor to make changes to policy settings set by the administrator.
Here is how you can do so and ensure that the Task Manager isn’t blocked for your account:
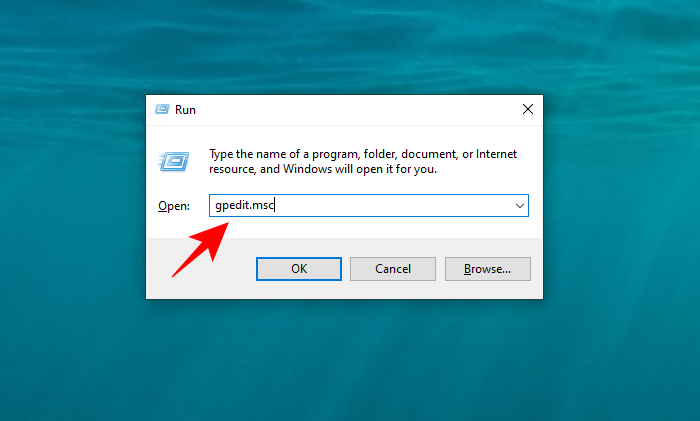
- Press
Win+Rto bring up the RUN box, type gpedit.msc and press Enter.
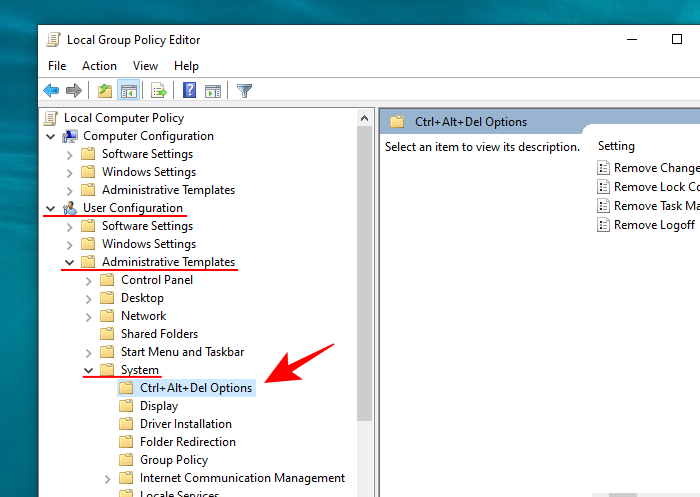
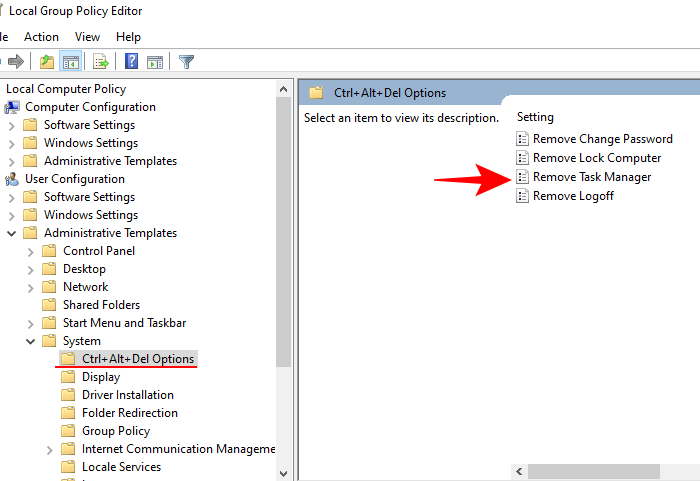
- Once the Group Policy Editor opens up, in the left panel, navigate to User Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Ctrl+Alt+Del Options.
- Now, in the right panel, double-click on Remove Task Manager.
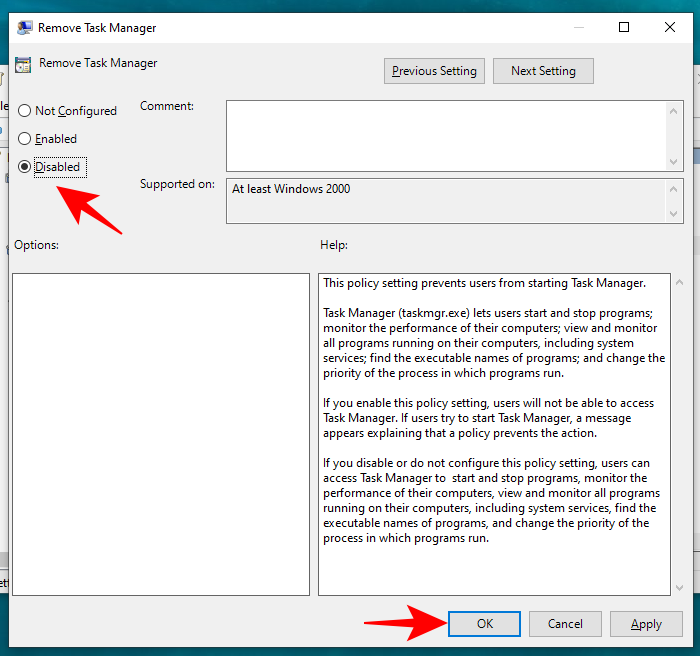
- Change the value to either “Not Configured” or “Disabled” to reactivate Task Manager for your account. Click OK.
- You may have to restart your computer and log back in to see the changes applied.
Note: Windows 11 Home users won’t be able to use this method as the Group Policy Editor is not available to them. They can, however, use the following methods to achieve the same result.
4. Unblock Task Manager using the Registry
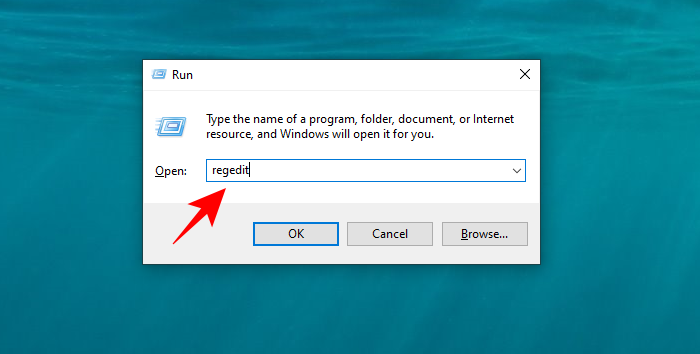
- Press
Win+Rto open the RUN box, type regedit and press Enter.
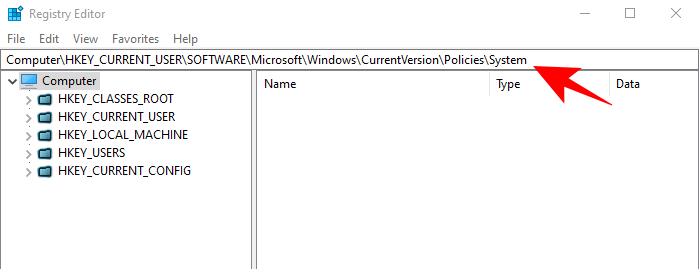
- Now, navigate to the following path:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System
Alternatively, you can simply copy the above path and paste it into the Registry’s address bar.
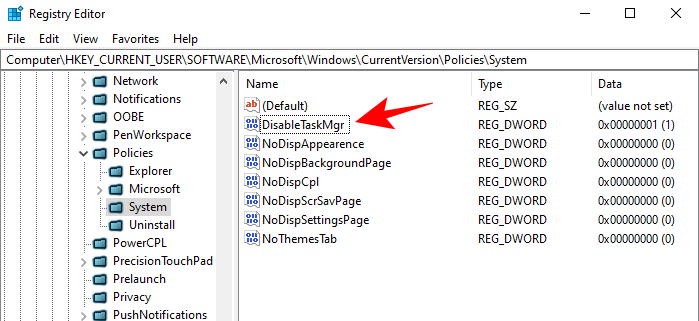
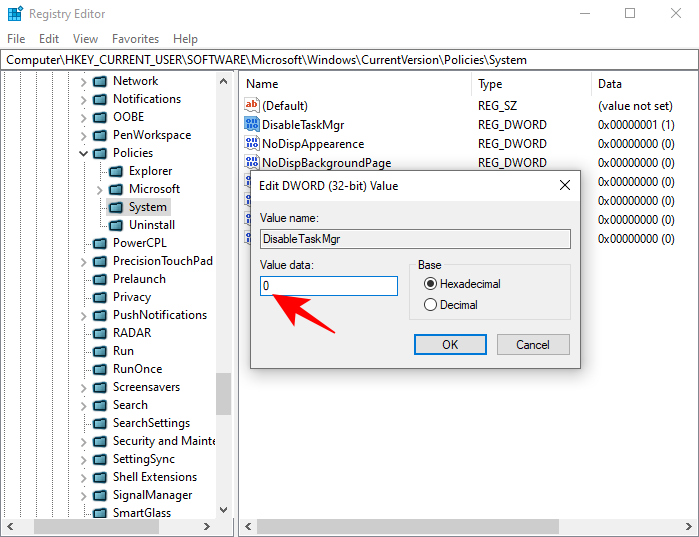
- Double-click the DisableTaskMgr key.
- Change the Value data from 1 to 0. Click OK.
You should now have access to the Task Manager through the Command Prompt as well as its shortcuts.
Show Process Command Lines in Task Manager
So now you can access Task Manager through the Command Prompt. Along with the different columns for CPU, Memory, Disk, and other resource columns, you can also engage a “Command Line” column. This helps to know the exact command for various processes and services that are running and make changes through the command prompt if need be. Here’s how you can enable it:
- Open the Task Manager, right-click on any column, and click on Command line.
- The column will now appear for the running Processes.
- You can similarly enable the Command Line column in the ‘Startup’ tab of the Task Manager as well.
- To enable the Command Line column in the “Details” tab, the method is slightly different. To do so, in the “Details” tab, right-click on any column and then on Select columns.
- This will bring up a small window. Scroll down until you find Command line. Check this box and click OK.
Knowing the command line of processes can help you terminate them (or restart them) through the Command Prompt.
So these were all the ways that you can access the Task Manager utility through the Command Prompt. Even if the task manager is blocked for your account, following these methods will ensure that you can unblock and have complete access to the Task Manager, through the shortcuts as well as the command prompt.










damn I want the arguments to the programs – not sure if they are accessible